Category: MS SQL
-

Big Data / NoSql
MongoDB Tutorials Tutorial 1 (guru99) Terms Quick Reference show dbs – show all dababases show collections – show all collections in database. use [db name] – switch to the specific database. db.[collection].find() – find records in the collection. db.[collection].find({email:”[email protected]”}) – find specific value db.[collection].findOne() – find one record in the collection. db.[collection].findOne({email:”[email protected]”},{password:”12345″}) – find specific…
-

Measure Ms Sql Execution time in resolution of milliseconds
DECLARE @t1 DATETIME; DECLARE @t2 DATETIME; SET @t1 = GETDATE(); /* Put here the query to measure */; SET @t2 = GETDATE(); SELECT DATEDIFF(millisecond,@t1,@t2) AS elapsed_ms;
-

Temporary tables and Table variables – MsSQL
Temporary Tables The simple answer is yes you can. Let look at a simple CREATE TABLE statement: CREATE TABLE #Yaks ( YakID int, YakName char(30) ) Temporary tables are created in tempdb. If you run this query: CREATE TABLE #Yaks ( YakID int, YakName char(30) ) select name from tempdb..sysobjects where name like ‘#yak%’ drop…
-
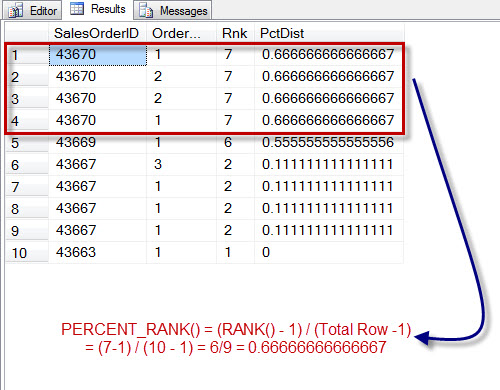
Ranking Functions
This article refers to AdventureWorks2014 of Microsoft. You can download AdventureWorks2014 DB here. At the following picture there are 4 ranking functions at MS SQL: 1. Row_number – Numbering each row. 2. Rank – According to example below when postal code change then the function displays the value of row_number at that position. 3. Dense_Rank –…
-

How to install PhpMyAdmin on C9.IO
here is a link of how to: https://docs.c9.io/docs/setting-up-phpmyadmin
-

Wise Owl: Microsoft computer training videos
At the following link you will find Video Tutorials of: 1. C# 2. SQL 3. SSIS 4. SSRS http://www.wiseowl.co.uk/videos/
-

How to search text at all Ms SQL tables, fields and all object?
1. Create the following Stored Procedure at the database you want to search: CREATE PROCEDURE SearchTables @Tablenames VARCHAR(500) ,@SearchStr NVARCHAR(60) ,@GenerateSQLOnly Bit = 0 AS /* Parameters and usage @Tablenames — Provide a single table name or multiple table name with comma seperated. If left blank , it will check for all the tables in…
-

A Beginner’s Guide to SQL
A great guide for learning SQL from the start, from Udemy: https://blog.udemy.com/beginners-guide-to-sql/ What Wikipedia has to say about UDemy: Udemy.com is a platform or marketplace for online learning. Unlike academic MOOC programs driven by traditional collegiate coursework, Udemy provides a platform for experts of any kind to create courses which can be offered to the public,…
-

SSMS / Visual Studio Sql server database project
Database good practice Tools to use: SSMS – sql server management studio Visual Studio The following video is the best to describe the process How To Create a Database Deployment Project in 10 minutes In short: Using VisualStudio connect to Database. Right click on the DB and select create new project. At this point there…
-

TECHNOLOGY TUTORIALS – kudvenkat
From kudvenkat: Over 12 years of experience, with Microsoft .NET technologies like ASP.NET, C#, SQL Server, AJAX, WCF, JQuery, SSIS, SSAS and SSRS. Currently working as a Technical Architect in central London. Love to share knowledge as I believe in “TO TEACH IS TO LEARN”. https://www.youtube.com/user/kudvenkat Got the opportunity to work on world’s largest e-commerce and…
-
The Connection Strings Reference
The Connection Strings Reference ConnectionStrings.com help developers connect software to data. It’s a straight to the point reference with connection strings, a knowledge base of articles and database connectivity content and a host of Q & A forums where developers help each other in finding solutions. http://www.connectionstrings.com/
-
MS SQL Server Editions
MS SQL Server Editions Also include Express editions http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/server-cloud/products/sql-server-editions/sql-server-express.aspx
-
SQL – How To Convert String To Datetime
How To Convert String To Datetime http://www.sqlusa.com/bestpractices/datetimeconversion/
-
How to find Object ID by name at SQL Server
How to find Object ID by name at SQL Server Example of how to find ID of tables at database according to tables name: SELECT * FROM sys.columns WHERE object_id = Object_id(’employees’)
-

What is SSAS? Analytic services learning resources
Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services, SSAS, is an online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining tool inMicrosoft SQL Server. SSAS is used as a tool by organizations to analyze and make sense of information possibly spread out across multiple databases, or in disparate tables or files. Microsoft has included a number of services in SQL…
-

All about SQL
Here you will find all you need regarding MS SQL: During the following Scripts, the following Databases will be used: 1. ACDB 2. hr_script 3. Northwind 4. AdventureWorks 2012 5. AdventureWorks 20146. AdventureWorks_2017 SQL Basics: 01 – SELECT-ALIAS-DISTINCT 02 – WHERE – ORDER BY – TOP 03 – SCALAR_FUNCTIONS 04 – GROUP BY – HAVING 05 -…
-

Instant SQL Formatter
This site will format your code and add colors a according to your source compiler. Here is an example: http://www.dpriver.com/pp/sqlformat.htm
-
Multiplication Table – Stored Procedure
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[Mulsp] @Size INT AS BEGIN DECLARE @X INT=2 DECLARE @Y INT=1 BEGIN try DROP TABLE [dbo].[multable] END try BEGIN catch END catch CREATE TABLE [dbo].[multable] ( c1 INT ) –create the rows DECLARE @CN NVARCHAR(max)=” DECLARE @TSql NVARCHAR(max) WHILE @x <= @Size BEGIN SELECT @cn = ‘c’ + Cast(@x AS NVARCHAR) PRINT @cn SET @TSql=‘alter table MulTable add ‘ + @cn + ‘ int’ PRINT @Tsql EXEC sys.Sp_sqlexec @Tsql SET @x=@x + 1 END –at this point build each line query SET @X=1 DECLARE @EachLineQuery NVARCHAR(max) WHILE @Y <= @Size BEGIN SET @EachLineQuery=‘insert into MulTable values (‘ WHILE @x < @Size BEGIN SET @EachLineQuery=@EachLineQuery + Cast(@x*@y AS NVARCHAR) + ‘,’ SET @x=@x + 1 END SET @EachLineQuery=@EachLineQuery + Cast(@x*@y AS NVARCHAR) + ‘)’ EXEC sys.Sp_sqlexec @EachLineQuery PRINT @EachLineQuery SET @EachLineQuery=” SET @y=@y + 1 SET @x=1 END SELECT * FROM multable END
-

w3schools.com – The world’s largest web development site
Offline version mediafire.com – w3schools.com.rar thecrazyprogrammer.com – w3schools-offline-version-download-full-website HTML HTML TutorialHTML Tag Reference CSS CSS TutorialCSS Reference JavaScript JavaScript TutorialJavaScript Reference SQL SQL TutorialSQL Reference PHP PHP TutorialPHP Reference JQuery JQuery TutorialJQuery Reference http://www.w3schools.com
-
Temp table Local / Global
— Create TEMP Table Local — Disappears when windows of query is closed. CREATE TABLE #tmp_table ( id INT, NAME VARCHAR(20) ) SELECT 1 AS ID, ‘John’ AS NAME — Create And Insert Into Temp Table INSERT INTO #tmp_table SELECT * FROM #tmp_table — Temp Table Global CREATE TABLE ##tmp_global_table — Create TEMP Table ( id INT, NAME VARCHAR(20) ) INSERT INTO ##tmp_global_table VALUES (1,’One’) SELECT * FROM ##tmp_global_table
-
Dynamic SQL – Demo of EXEC and sp_executesql
This demo s pretty self explained, you just copy and paste it into SQL Management studio: DECLARE @cmd NVARCHAR(30) = ‘SELECT * FROM Person.Address’ EXEC (@cmd) go — Using Dynamic SQL With Parameter DECLARE @cmd_param VARCHAR = 1 DECLARE @cmd VARCHAR(100) = N’Select * from employees where employeeid = ‘ + @cmd_param EXEC (@cmd) — DDL – Create Table DECLARE @cmd VARCHAR(100) SET @cmd = ‘Create table TBL (col1 int)’ EXEC (@cmd) SELECT * FROM tbl; — DROP DROP TABLE tbl — sp_executesql — DECLARE @cmd NVARCHAR(100) SET @cmd = ‘SELECT * FROM Person.Address where AddressID = @1 and PostalCode = @2′ EXEC Sp_executesql @cmd, N’@1 int, @2 nvarchar(15)’, 1, ‘98011’ go
-
Can’t browse SDF files in Visual Studio 2013
In Visual Studio 2013 you could double click a SDF database file within Solution Explorer and it would automatically open the database file and allow you to view the database tables, add tables, edit data etc. In Visual Studio 2013 this native support seems to have ‘fallen off’, double clicking an SDF file simply assumes it…